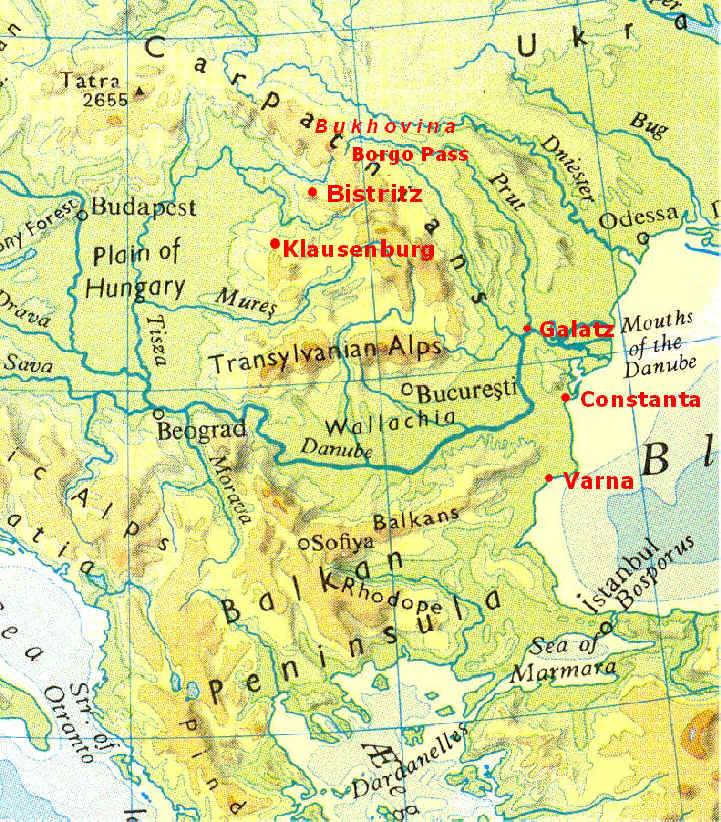
Fallen Angel Theatre Map of Places Mentioned in Dracula |
|
| Some of the place names have changed since Dracula
was writtten. For example: Klausenburg, Bistritz and Galatz are all German place
names reflecting the medieval Transylvanian Saxon settlement and later Habsburg influence
in what is now Romania. Following the the First World War and the disintegration of the
Austro-Hungarian Empire, many towns became known by the local language version of their
names. Thus Klausenburg became Cluj-Napoca, Bistritz became Bistrita, and Galatz became Galati.
Bistritz (Bistrita) is the capital city of Bistrita-Nasaud County, Transylvania. Transylvanian Saxons settled the area in 1206. Being situated on several trade routes, Bistrita became a flourishing medieval trading post. The town was named after the Bistrita River, whose name comes from the Slavic word bystrica meaning "the limpid water". In Dracula, Jonathan Harker stays at the Golden Krone Hotel (Romanian: Coroana de Aur) in Bistritz. Although no such hotel existed when the novel was written, a hotel of the same name has since been constructed for tourists.
Borgo Pass. The Borgo or Tihu ta Pass (Romanian: Pasul Tihuta; Hungarian: Borgo or Burgo) (el. 1201 m.) is a high mountain pass in the Romanian Bârgau Mountains (Eastern Carpathian Mountains) connecting Bistrita (Transylvania) with Vatra Dornei (Bukovina, Moldovia). The pass was made famous by Bram Stoker's novel Dracula where, termed as the "Borgo Pass", it was the gateway to the realm of Count Dracula.
Buda-Pesth is of course Budapest. The hyphenated nineteenth century name reflects the city's (then) recent origin from the union of two cities, Buda and Pest(h) on opposite banks of the River Danube. When Charles V of Lorraine conquered them for the Hapsburgs in 1686, both Buda and Pest were in ruins. They were resettled, Buda with Germans, Pest with Serbs and Hungarians. Buda, a free royal town after 1703, had a renaissance under Maria Theresa, who built a royal palace and in 1777 transferred to Buda the university founded in 1635 by Peter Pazmany at Nagyzombat. The university was later moved (1784) to Pest. In the 19th cent. Pest flourished as an intellectual and commercial center; after the flood of 1838, it was rebuilt on modern lines. Buda became largely a residential sector. After the union of Buda and Pest in 1873, the united city grew rapidly as one of the two capitals of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy. Budapest became famed for its literary, theatrical, and musical life and attracted tourists with its mineral springs, its historic buildings, and its parks. With the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy (Oct., 1918), Hungary was proclaimed an independent republic. Budapest became its capital.
Bukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains. It is currently split between Romania and Ukraine.
Constanta is a port on the Black Sea and is the oldest city in Romania. A number of inscriptions found in the town and its vicinity show that Constanta lies where once Tomis stood. Tomis was a Greek colony on the Black Sea's shore, founded around 500 BC An impressive public building, thought to have originally been a port building, has been excavated, and contains the substantial remains of one of the longest mosaic pavements in the world. In 1878, after the Romanian War of Independence, Constanta and the rest of Northern Dobruja were ceded by the Ottoman Empire to Romania. The city became Romania's main seaport and transit point for much of Romania's exports.
Dardanelles formerly known as the Hellespont, is a narrow strait in northwestern Turkey connecting the Aegean Sea to the Sea of Marmara and thence the Mediterranean to the Black Sea. Like the Bosporus, the Dardanelles separates Europe (in this case the Gallipoli peninsula) and the mainland of Asia. The strait has long had a strategic role in history. The ancient city of Troy was located near the western entrance of the strait and the strait's Asiatic shore was the focus of the Trojan War. The Persian army of Xerxes I and later the Greek army of Alexander the Great crossed the Dardanelles in opposite directions to invade each other's lands. Gaining control or special access to the strait became a key foreign policy goal of the Russian Empire during the 19th century. The United Kingdom and France subsequently sent their fleets through the straits to attack Crimea during the Crimean War in 1853—but this was done as allies of the Ottoman Empire. In the First World War The western Allies sent a massive invasion force of troops to attempt to open up the strait. At the battle of Gallipoli, Turkish troops trapped the Allies on the beaches of the Gallipoli peninsula resulting in a military disaster.
Galatz (Galati) is a port on the lower Danube which is accessible both by river boats and ocean-going ships via the Black sea.
Klausenburg (Cluj-Napoca) is the capital of the historical province of Transylvania. From 1790 to 1848 and again from 1861 to 1867, Klausenburg was the capital of the Grand Principality of Siebenbürgen within the Austrian EmpireAfter the Ausgleich (compromise) which created Austria-Hungary in 1867, Klausenburg and Transylvania were again integrated into the Kingdom of Hungary. In 1897, the Hungarian government decided that only Hungarian place names should be used and therefore prohibited the use of the German or Romanian versions of the city's name in official government documents. In 1872, the authorities established a University, with teaching exclusively in Hungarian, which caused discontent amongst the Romanian population. In 1881 the University was renamed Franz Joseph University after Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria. After World War I, Klausenburg (Cluj) became part of the Kingdom of Romania, along with the rest of Transylvania.
Pruth or Prut is a river in Eastern Europe. It originates on the eastern slope of Mount Hoverla, in the Carpathian Mountains. It runs parallel to the Siret (see below) and flows southeast to join the Danube river near Reni, east of Gala ti.
Sereth or Siret is a river that rises from the Carpathians in the Northern Bukovina region, and flows southward into Romania for 470 km before it joins the Danube at Galatz. The headwaters are near the Borgo Pass.
Varna is a port on the Black Sea , it is among Europe's oldest cities. In 339 BCE, the city was unsuccessfully besieged by Philip II but surrendered to Alexander the Great in 335 BC. The Roman city, Odessus, occupied 47 hectares in present-day central Varna and had prominent public baths, Thermae, erected in the late 2nd century, now the largest Roman remains in Bulgaria and fourth-largest known Roman baths in Europe. The British and French campaigning against Russia in the Crimean War (1854-1856) used Varna as headquarters and principal naval base. In 1866, the first railroad in Bulgaria connected Varna with Rousse on the Danube, linking the Ottoman capital Istanbul with Central Europe; for a few years, the Orient Express ran through that route. The port of Varna developed as a major supplier of food—notably wheat from the adjacent breadbasket Southern Dobruja—to Istanbul and a busy hub for European imports to the capital. With the national liberation in 1878, the city was ceded to Bulgaria. |